Spatiotemporal changes of eutrophication and heavy metal pollution
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 16 novembro 2024
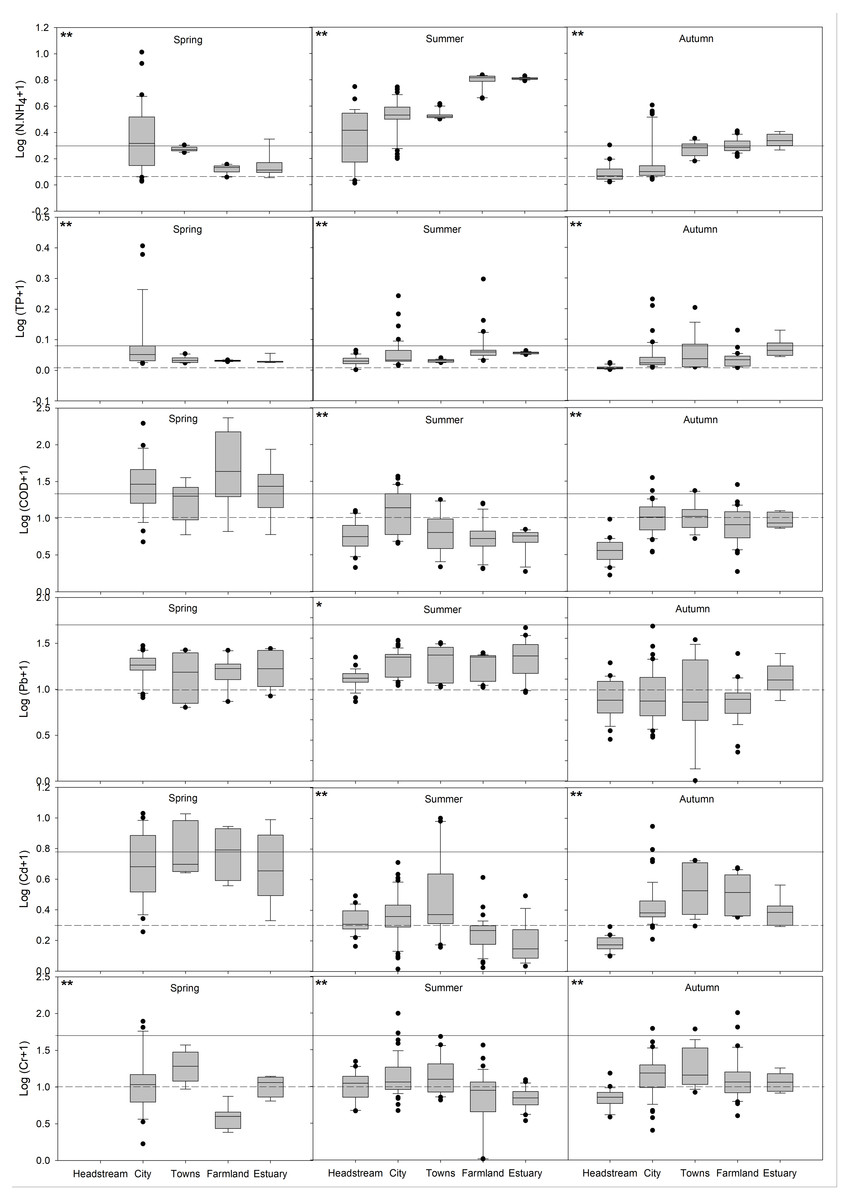
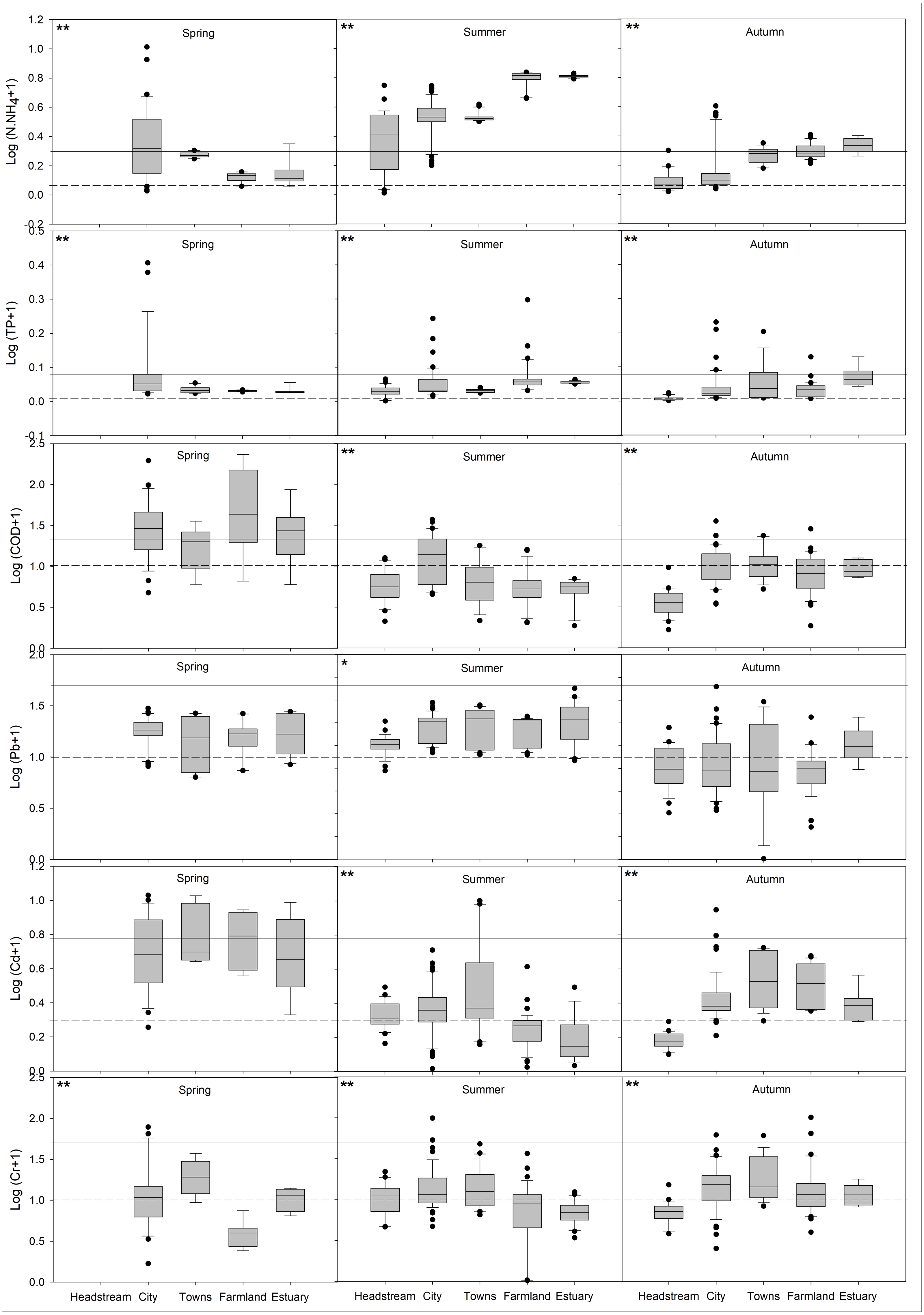
Pollution in inflow rivers seriously endangers the water environment in downstream lakes. In this study, an inflow river system of the Baiyangdian–Fuhe river system (FRS) was investigated to display timely pollution patterns of eutrophication and heavy metals after the establishment of Xiongan New Area, aiming to reveal the weak parts in current pollution treatments and guide the further water quality management. The results showed that the pollution of eutrophication was worse than the heavy metals in FRS, with serious eutrophic parameters of ammonia nitrogen (NH4+-N) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). There were greatly spatiotemporal variations of the pollution in FRS. (1) Concentrations of NH4+-N and total phosphorus were all higher in summer and autumn, whereas, COD contents were higher in spring; the water quality index (WQI) of eutrophication linearly increased along FRS in summer and autumn, with pollution hotspots around the estuary area. (2) The pollution levels of plumbum exceeded cadmium (Cd) and chromium (Cr) but without strongly spatiotemporal changes; however, Cd and Cr in the town area and Cd in spring showed higher concentrations; the WQI of heavy metals showed single peak curves along FRS, with significantly higher values around the town area. Additionally, the four potential pollution sources: domestic sewage, traffic pollution, agricultural wastewater and polluted sediments were identified based on the pollution patterns and pollutant associations. These findings demonstrated current treatments failed to eliminate the pollution in some hotspots and periods, and the in-depth understanding of the pollution spatiotemporal patterns in this study, especially the pollution hotspots, serious periods and potential sources, are crucial to furtherly develop spatiotemporally flexible pollution treatment strategies.
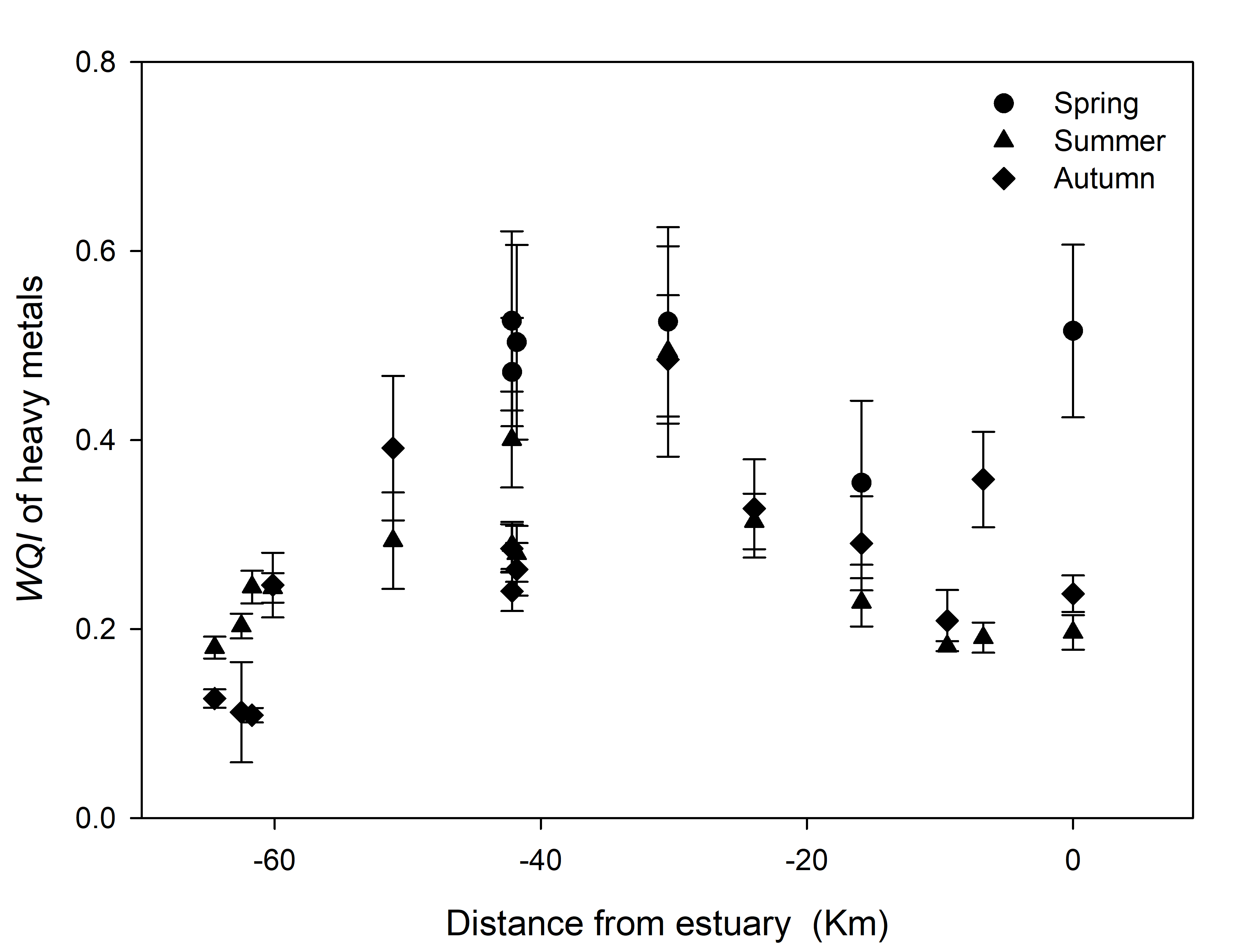
Spatiotemporal changes of eutrophication and heavy metal pollution in the inflow river system of Baiyangdian after the establishment of Xiongan New Area [PeerJ]

Identifying spatio-temporal dynamics of trace metals in shallow eutrophic lakes on the basis of a case study in Lake Taihu, China - ScienceDirect
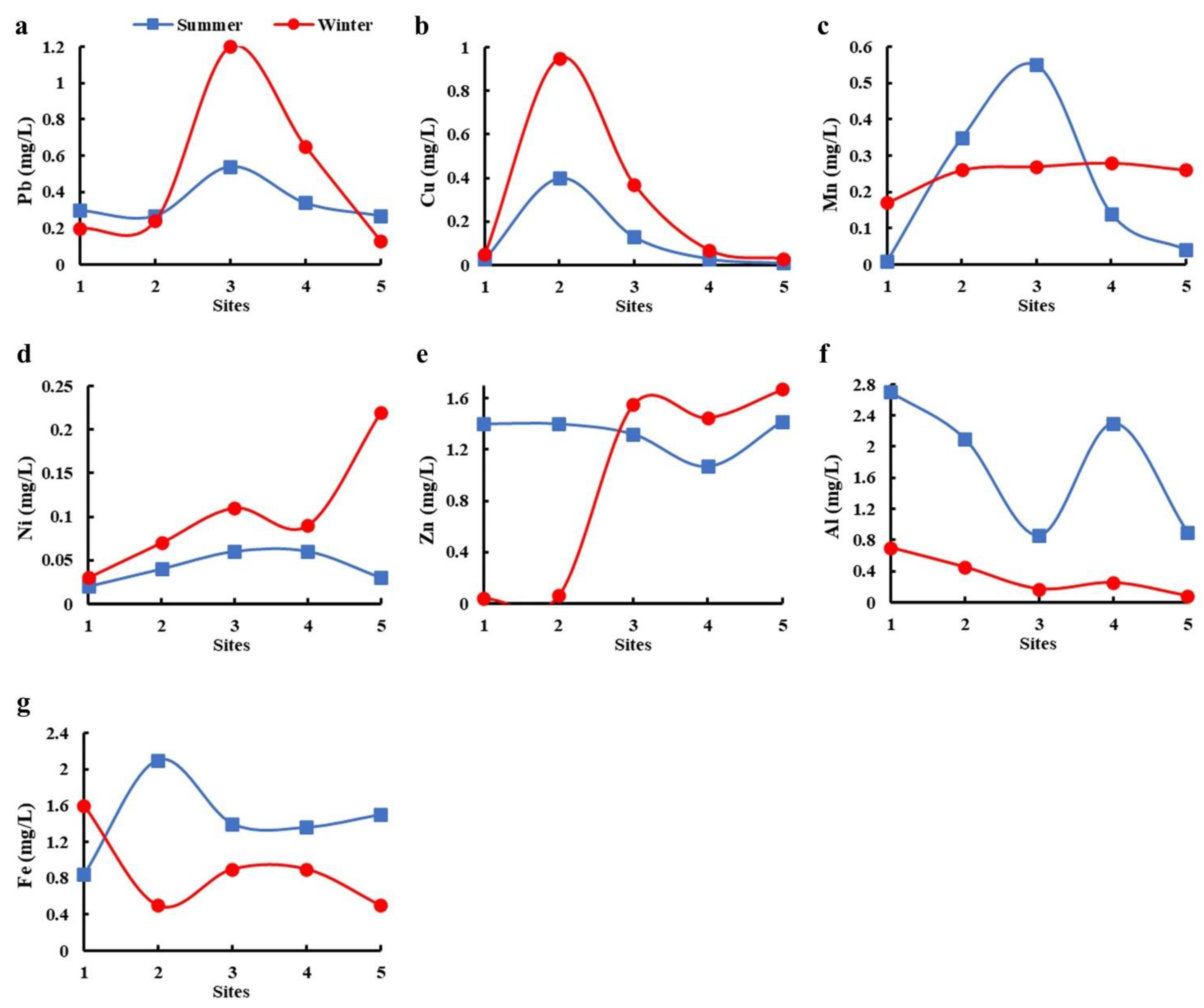
Water, Free Full-Text

Spatio-temporal evolution of eutrophication and water quality in the Turawa dam reservoir, Poland

Spatiotemporal variations of heavy metal historical accumulation records and their influencing mechanisms in the Yangtze River Estuary - ScienceDirect

Spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and sediment phosphorus content of a large reservoir in Turkey - ScienceDirect
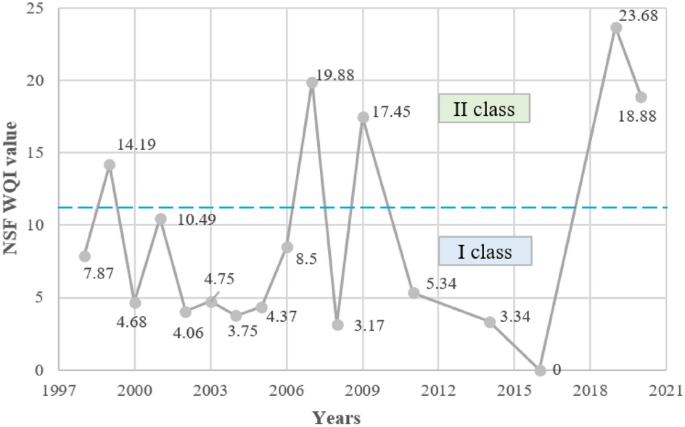
Spatio-temporal evolution of eutrophication and water quality in the Turawa dam reservoir, Poland

Changes of six possible pollution sources in the Honghu Basin from 2004
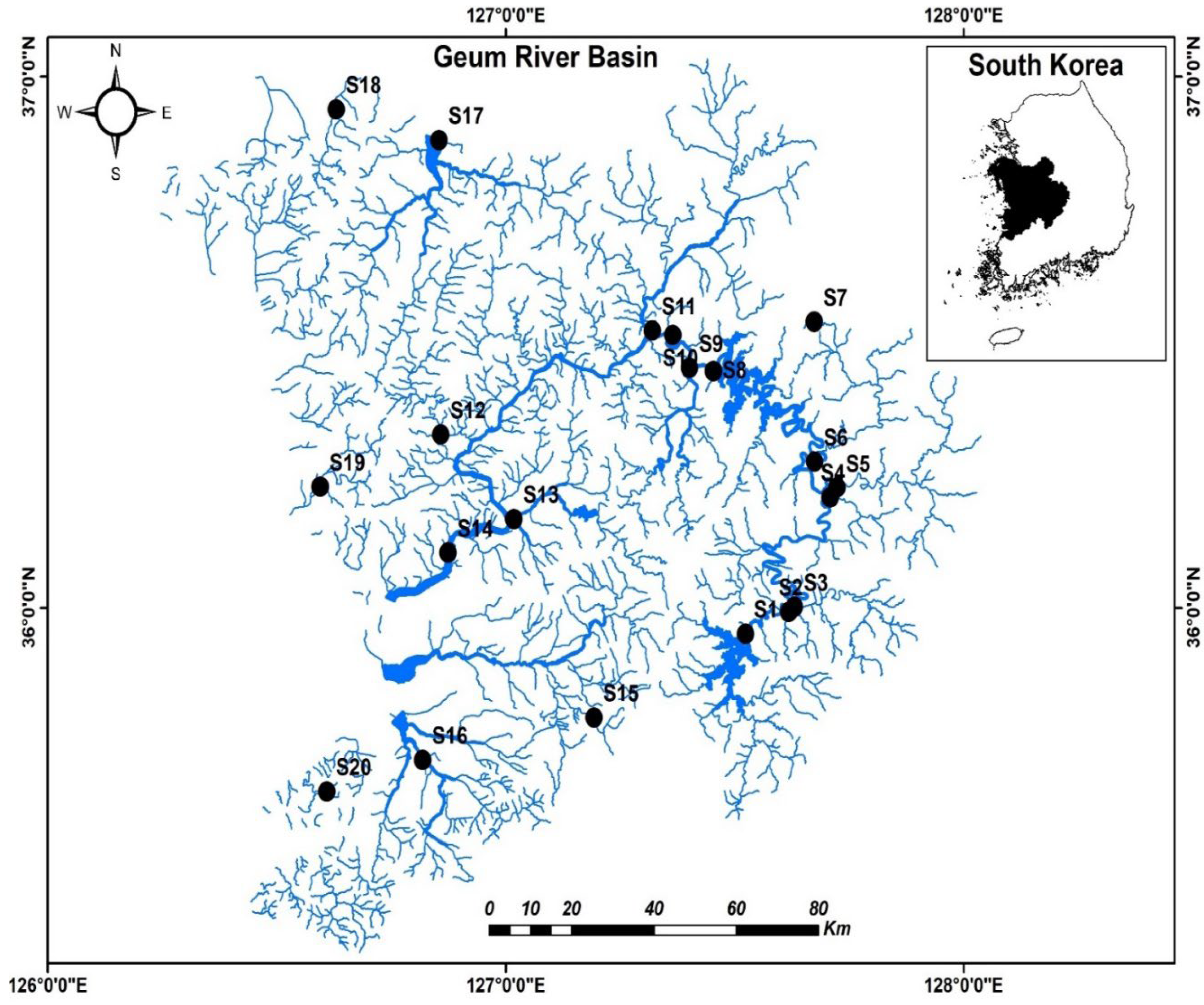
Water, Free Full-Text
Spatiotemporal changes of eutrophication and heavy metal pollution in the inflow river system of Baiyangdian after the establishment of Xiongan New Area [PeerJ]

Appraisal of heavy metal contents, spatial–temporal variation, toxic metal pollution, and health risk in water and sediment of Uluabat Lake (Ramsar Site, Turkey)

Spatiotemporal changes of eutrophication and heavy metal pollution in the inflow river system of Baiyangdian after the establishment of Xiongan New Area [PeerJ]
Recomendado para você
você pode gostar





![Paramore: I'm not angry anymore [interlude] ukulele chords —- this](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/06/f6/77/06f6776ec393a06e8ad02d4855ccb9ec.jpg)





![Koi to producer : Evol X love episode 12 Eng sub [Mr Love: Queen's Choice] FULL HD](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4dEvkIGmd6Q/maxresdefault.jpg)