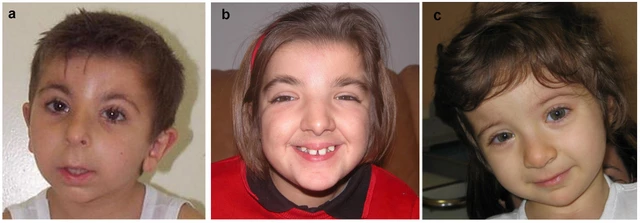
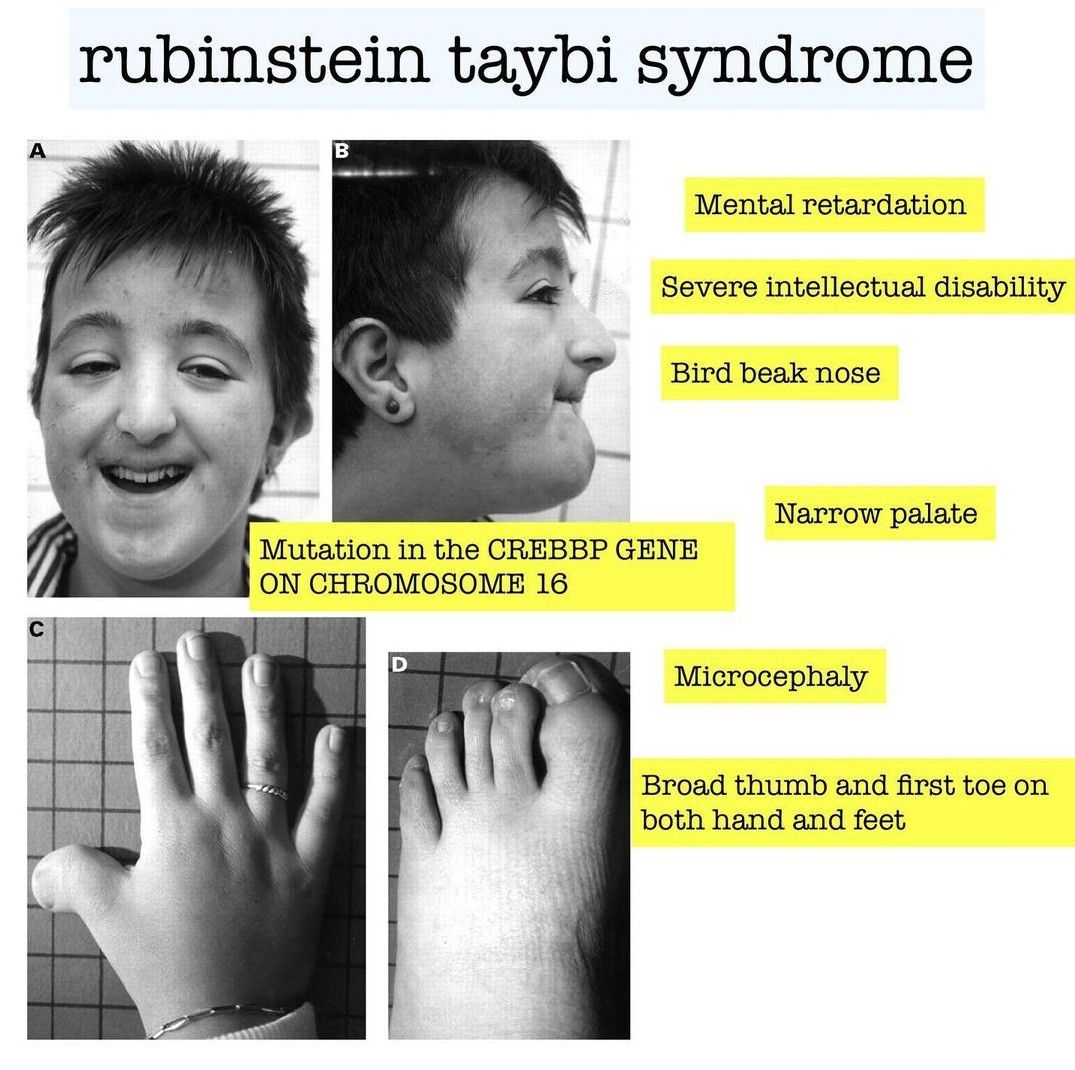
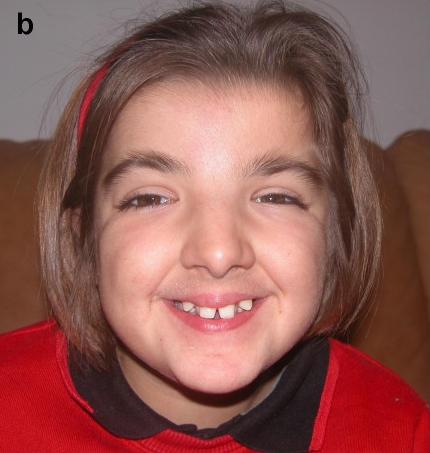
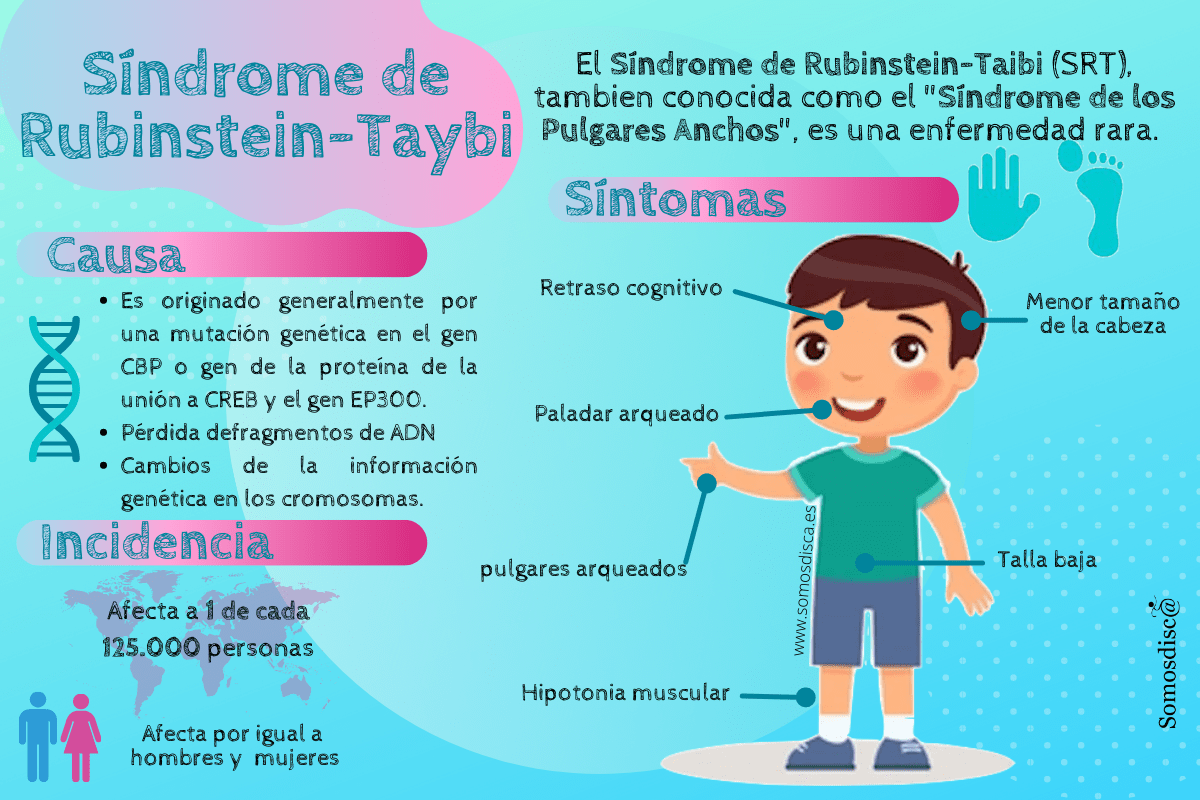
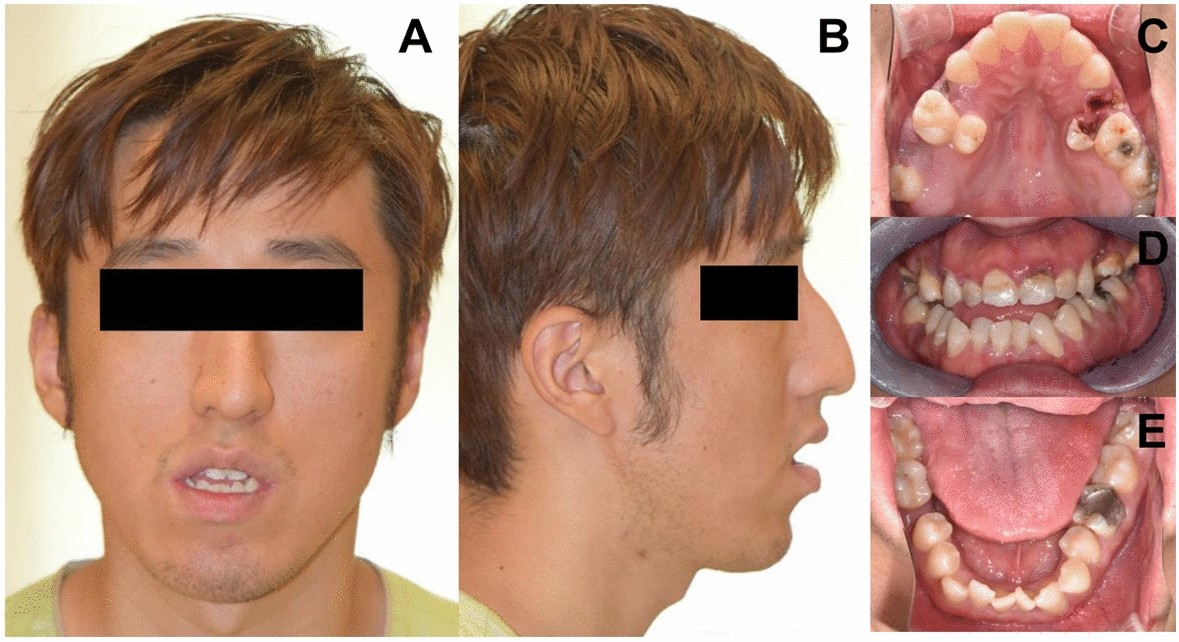
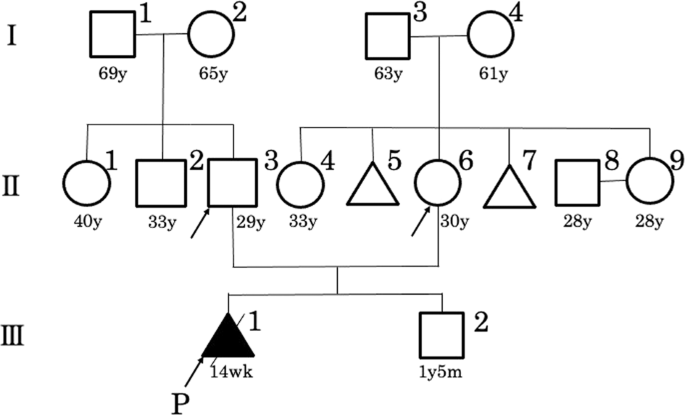
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 20 setembro 2024
Novel missense COL2A1 variant in a fetus with achondrogenesis type II
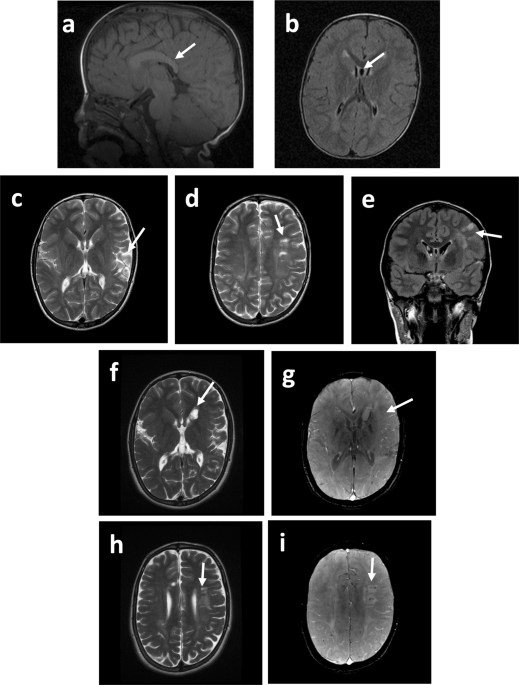
A novel de novo MTOR gain-of-function variant in a patient with Smith-Kingsmore syndrome and Antiphospholipid syndrome
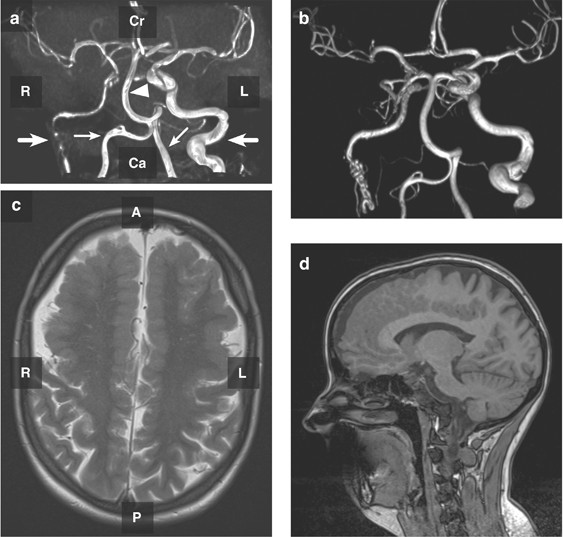
Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome in siblings with biallelic COL3A1 sequence variants and marked clinical variability in the extended family
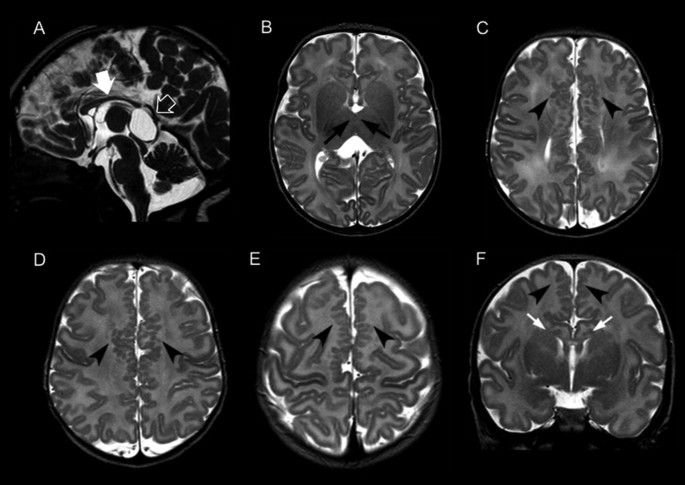
Malformations of Cortical Development

Depiction of amino acid residues in the HAT region (A) and CH1 region

Activation of human or salmon plasminogen by human uPA or zfuPA-a or

Protein-protein interaction network describes the possible interaction

Nuclear Localization signals (NLSs) predicted by PSORTII [21] analysis.

Otopalatodigital Syndrome, Type Ii disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials

Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP300
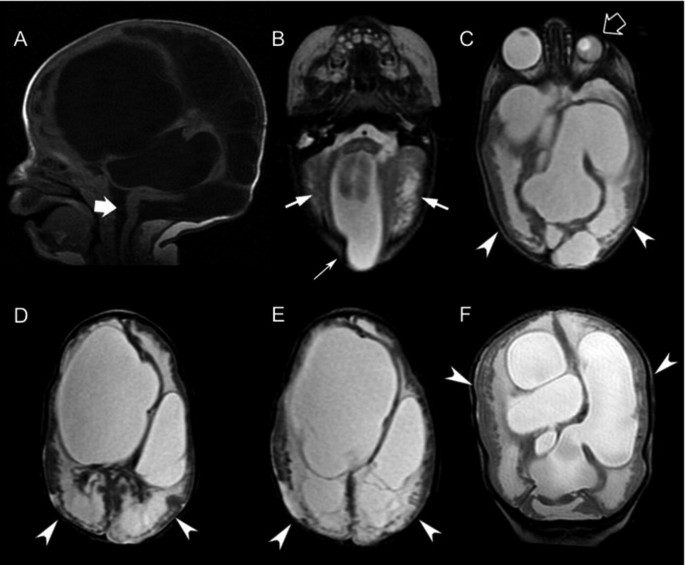
Malformations of Cortical Development

Subclass IgG levels of patients with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome compared
Segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation and epidermal nevus (SOLAMEN) syndrome is related to mosaic PTEN nullizygosity
Recomendado para você
você pode gostar