Comparing Labetalol and Nitroglycerine on Inducing Controlled Hypotension and Intraoperative Blood Loss in Rhinoplasty: A Single-Blinded Clinical Trial, Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 10 novembro 2024
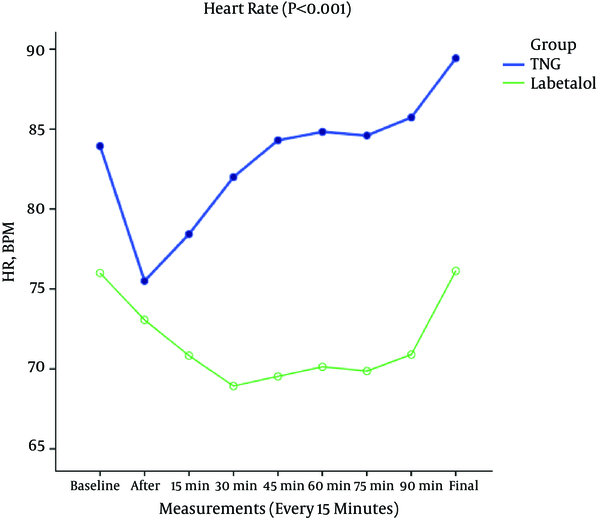
Background: Uncontrolled bleeding during surgery is one of the main predisposing factors for failure of the surgeon and complications following rhinoplasty. The current study aimed at comparing the effects of nitroglycerine and labetalol on the induction of controlled hypotension and bleeding volume during septorhinoplasty. Methods: The current randomized, controlled, clinical trial enrolled 60 patients candidate for septorhinoplasty at Firoozgar hospital in Tehran, Iran, in 2 equal groups receiving either 0.1 to 1 mcg/kg/minute nitroglycerine or 2 to 4 mg/minute labetalol to achieve a mean arterial blood pressure of about 60 to 65 mmHg. In case the targeted blood pressure was not achieved, isoflurane was added. Degree of bleeding was evaluated by the volume of suctioned blood and the blood remaining in surgical gauzes. Additionally, the surgeon's satisfaction with the surgical field was evaluated by a scoring system. The collected data were, then, compared between the study groups by the statistical methods. Results: Based on the current study findings, systolic (P < 0.001), diastolic (P = 0.002), and the mean arterial blood pressures (P < 0.001) were significantly lower in the nitroglycerine group. Ninety percent of the patients in the labetalol group received isoflurane to achieve the targeted blood pressure defined as controlled hypotension. There was no significant difference between the groups regarding the volume of bleeding (P = 0.75); however, the surgeons were more satisfied with nitroglycerine than labetalol (P < 0.001). Conclusions: It was concluded that nitroglycerine had a better effect, in comparison to labetalol, on inducing the controlled hypotension in septorhinoplasty.

PDF] Effects of Premedication with Metoprolol on Bleeding and

PDF) Comparative Study of Blood Loss, Quality of Surgical Field
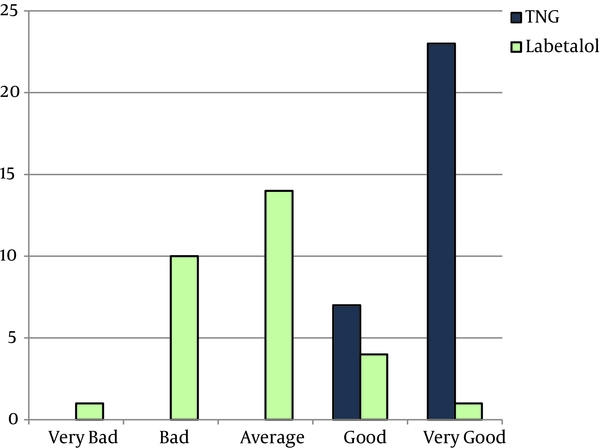
Comparing Labetalol and Nitroglycerine on Inducing Controlled
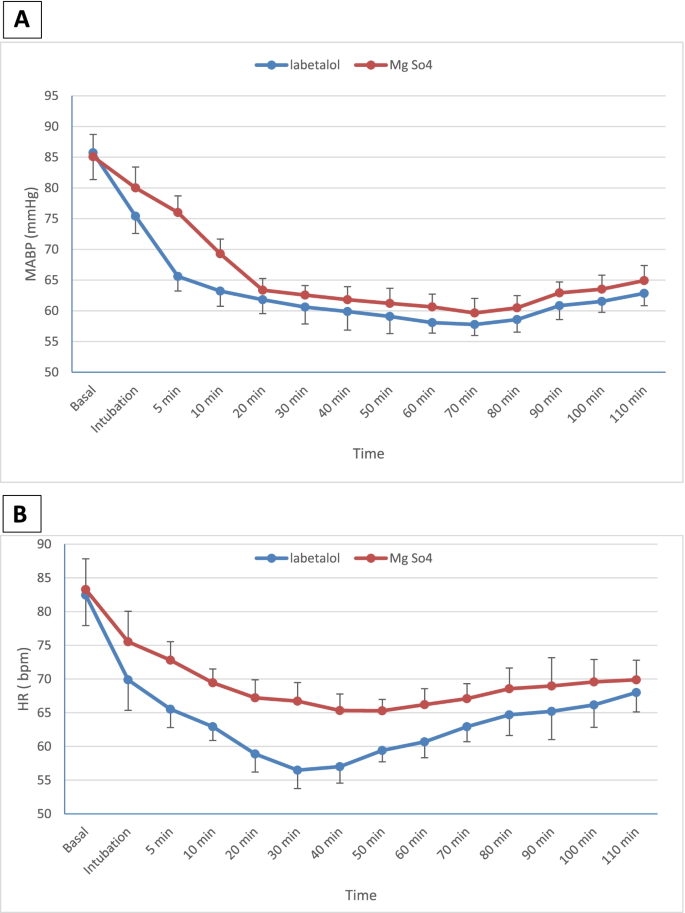
Effect of perioperative magnesium sulfate and labetalol infusion

Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology

Nitroglycerine, esmolol and dexmedetomidine for induced

Comparison of Labetalol, Nitroglycerine and High Dose Propofol for
PDF) To Compare the Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine Versus Labetalol

Effect of Different Loading Doses of Dexmedetomidine on Controlled
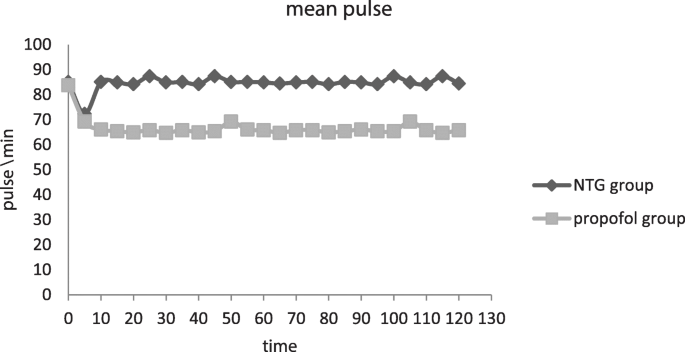
Comparison of the hypotensive efficacy of propofol infusion versus
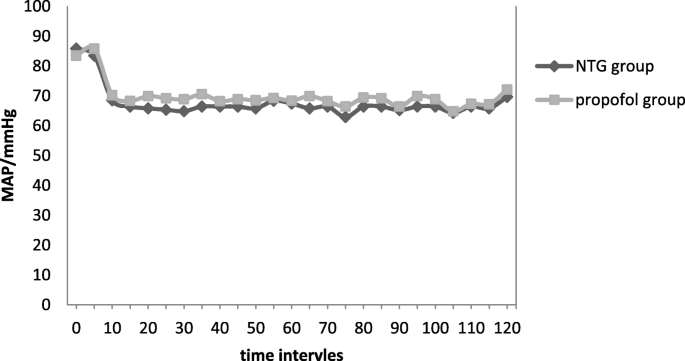
Comparison of the hypotensive efficacy of propofol infusion versus

DOC) SYNOPSIS OF DISSERTATION A COMPARATIVE CLINICAL STUDY OF
Recomendado para você
você pode gostar