Guilt of the Meat‐Eating Consumer: When Animal Anthropomorphism Leads to Healthy Meat Dish Choices - Kim - 2021 - Journal of Consumer Psychology - Wiley Online Library
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 11 novembro 2024


What's the beef?: Debating meat, matters of concern and the emergence of online issue publics - ScienceDirect

PDF) Bring it on! Package shape signaling dominant male body promotes healthy food consumption for male consumers

Animals are friends, not food”: Anthropomorphism leads to less favorable attitudes toward meat consumption by inducing feelings of anticipatory guilt - ScienceDirect

Foods, Free Full-Text

Animals are friends, not food”: Anthropomorphism leads to less favorable attitudes toward meat consumption by inducing feelings of anticipatory guilt - ScienceDirect

Personal or planetary health? Direct, spillover and carryover effects of non-monetary benefits of vegetarian behaviour - ScienceDirect

Should We Eat Meat?: Evolution and Consequences of Modern Carnivory: Smil, Vaclav: 9781118278727: : Books

Meat consumption, health, and the environment

The effect of disease anthropomorphism on compliance with health recommendations

Appealing to Gen Z with Mother Nature for sustainable consumption: With mediation of psychological closeness to nature and consequence of psychological well‐being - Jeong - Journal of Consumer Behaviour - Wiley Online Library

The role of vending channels in marketing: A systematic review and taxonomy of studies - Stoyanov - 2021 - Journal of Consumer Affairs - Wiley Online Library

The effects of food anthropomorphism on consumer behavior: A systematic literature review with integrative framework and future research directions - ScienceDirect
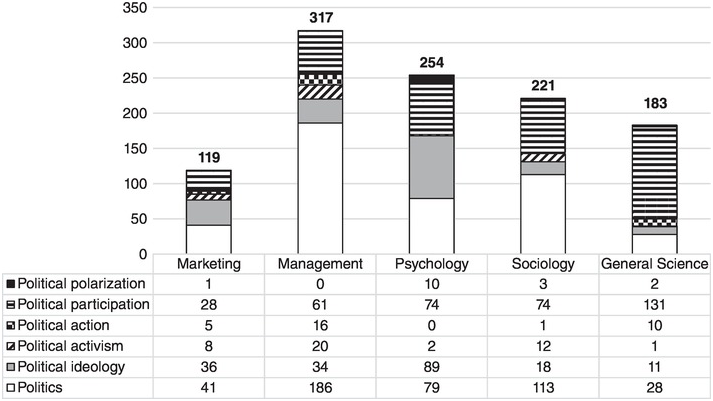
Consumer Psychology of Groups and Society (Chapter 2) - The Cambridge Handbook of Consumer Psychology

Animals are friends, not food”: Anthropomorphism leads to less favorable attitudes toward meat consumption by inducing feelings of anticipatory guilt - ScienceDirect
Recomendado para você
você pode gostar