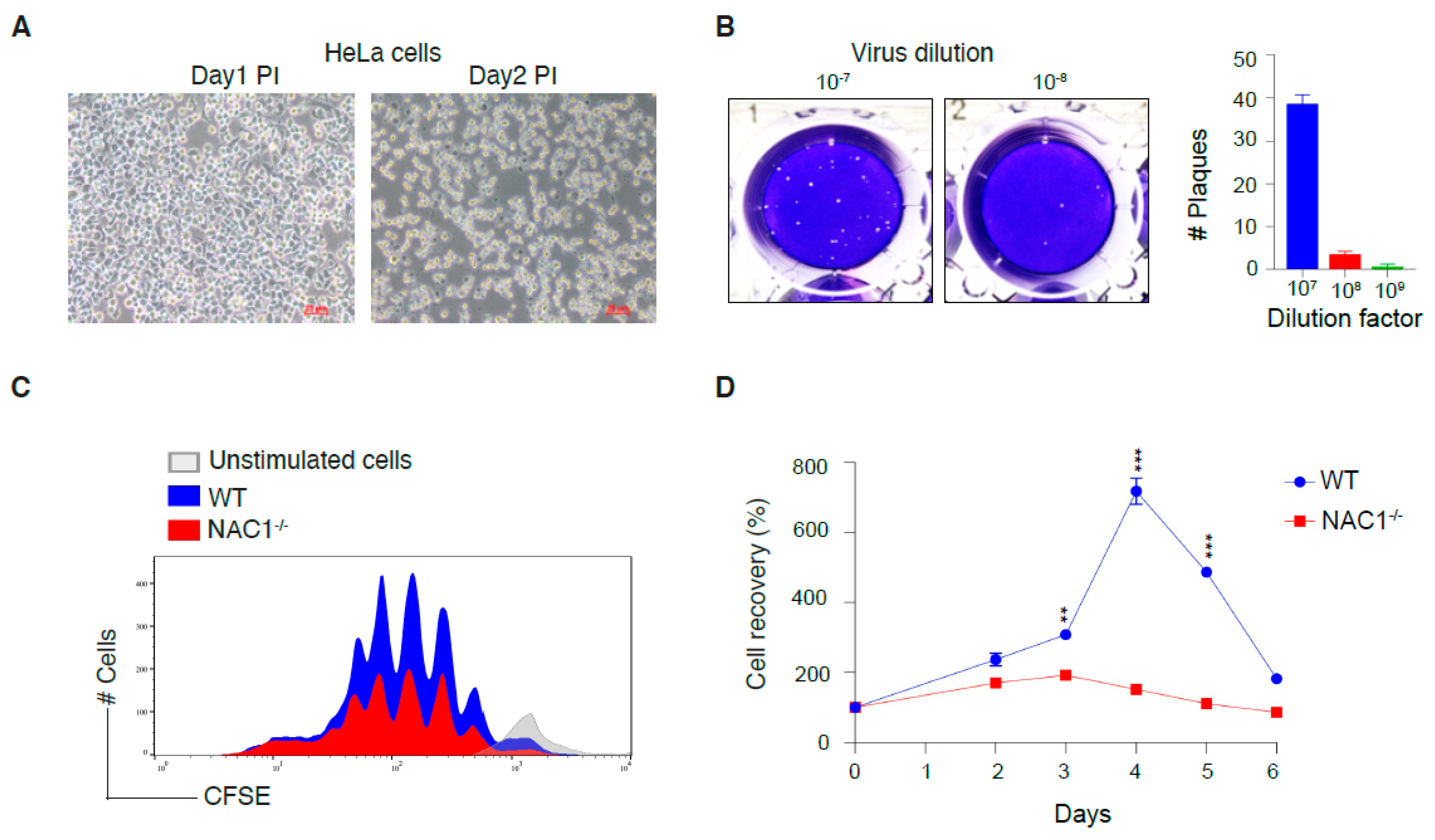
Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 06 outubro 2024
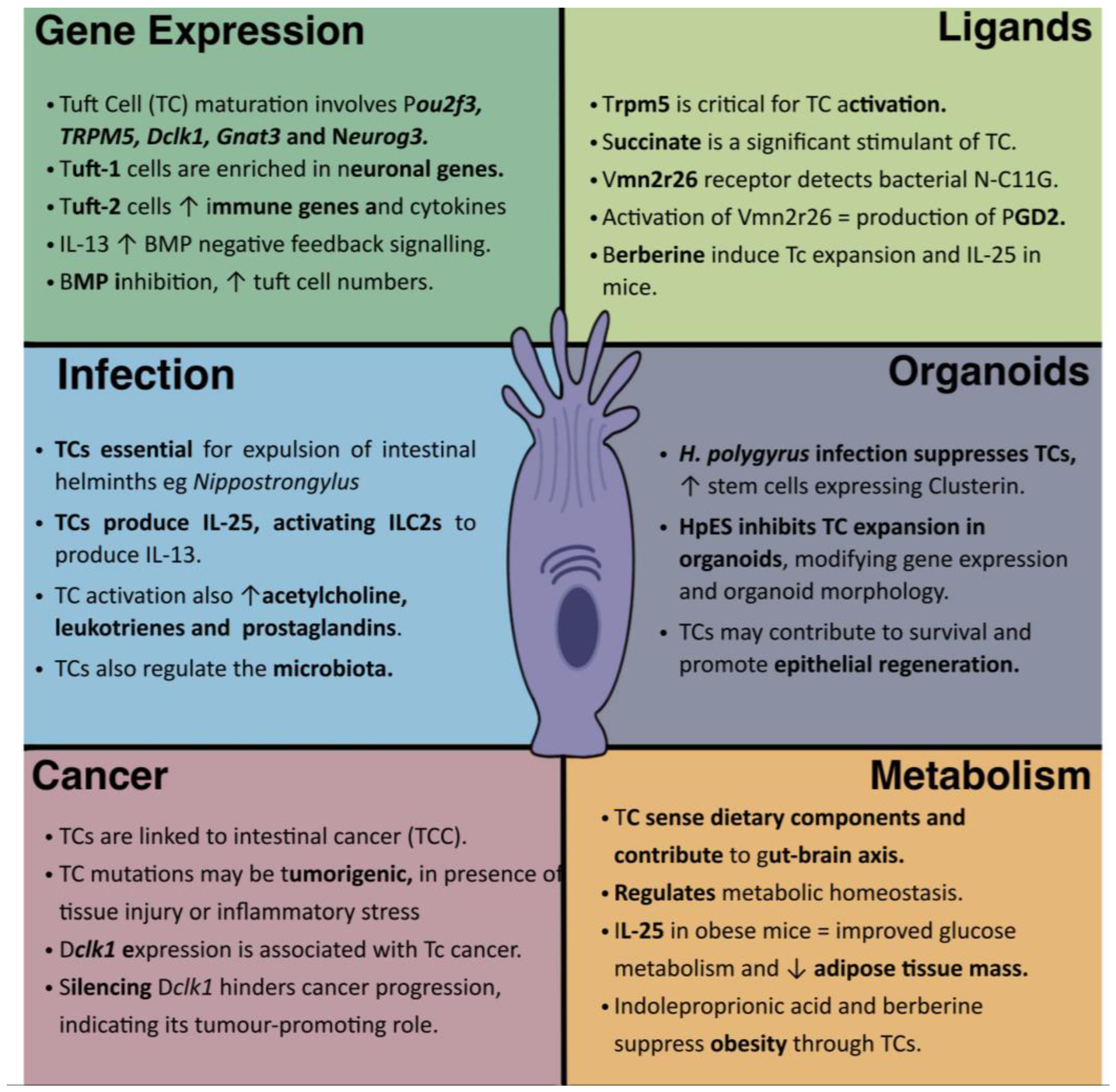
Tuft cells have recently emerged as the focus of intense interest following the discovery of their chemosensory role in the intestinal tract, and their ability to activate Type 2 immune responses to helminth parasites. Moreover, they populate a wide range of mucosal tissues and are intimately connected to immune and neuronal cells, either directly or through the release of pharmacologically active mediators. They are now recognised to fulfil both homeostatic roles, in metabolism and tissue integrity, as well as acting as the first sensors of parasite infection, immunity to which is lost in their absence. In this review we focus primarily on the importance of tuft cells in the intestinal niche, but also link to their more generalised physiological role and discuss their potential as targets for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
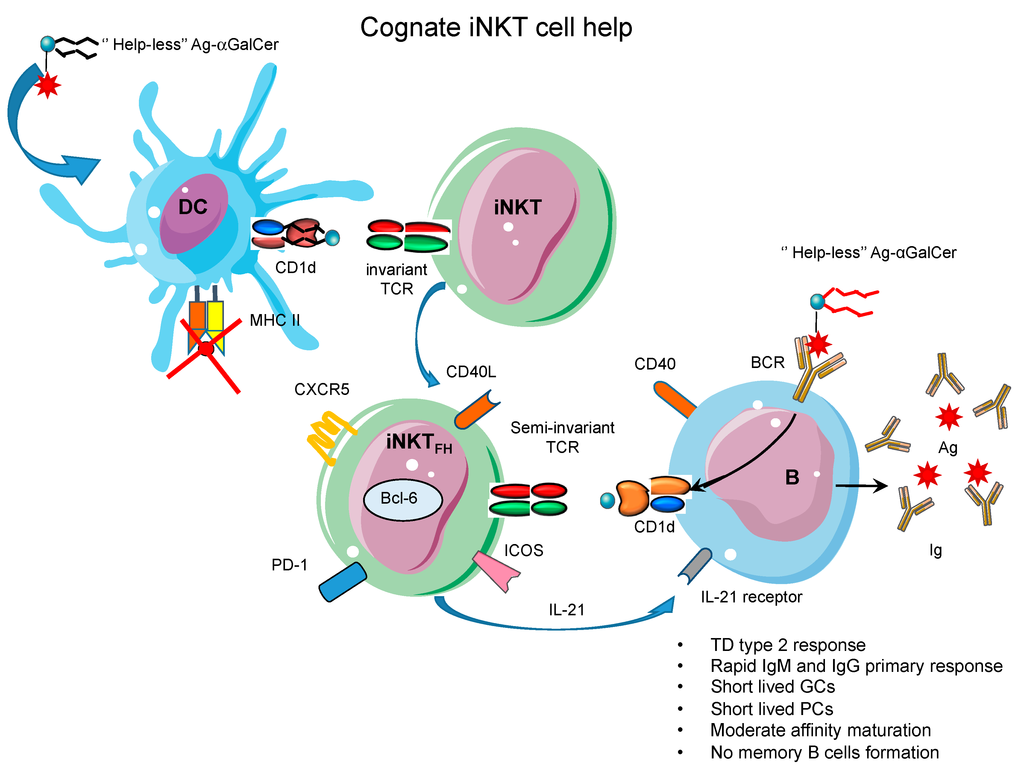
Antibodies, Free Full-Text

Cell-Free DNA and Apoptosis: How Dead Cells Inform About the Living - ScienceDirect

Cell-Free Translation Systems

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy

Nucleic acid biomarkers of immune response and cell and tissue damage in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C - ScienceDirect
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.
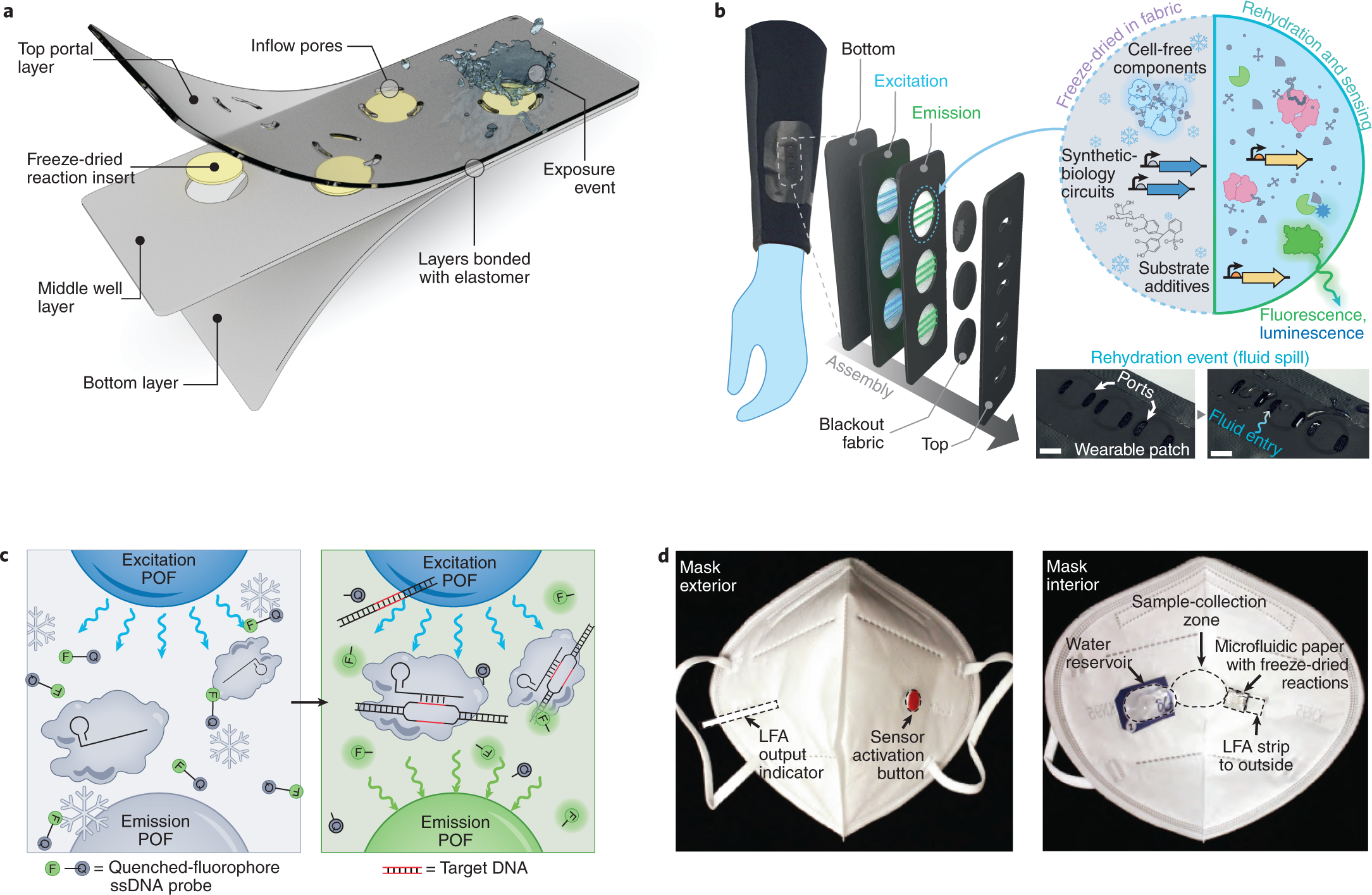
Textile-embedded cell-free biosensors

Cells, Free Full-Text
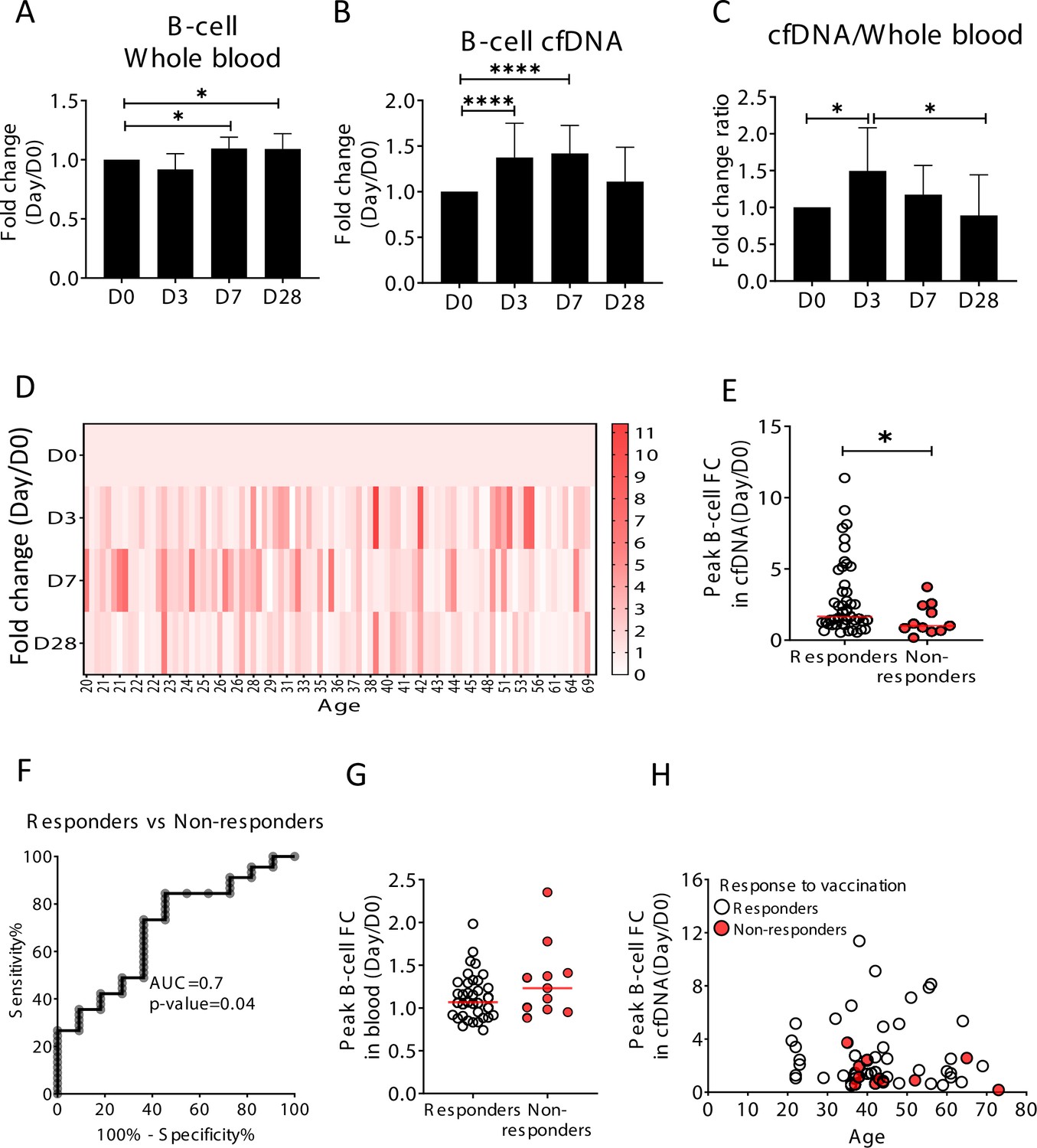
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA
Recomendado para você
você pode gostar